"Banking at Your Fingertips: How Digital Banking is Changing the Game in Malaysia"
Published byDigital banking refers to the use of digital technologies to offer banking services to customers. It encompasses a range of digital channels and services, including online banking, mobile banking, and other digital banking platforms. In the context of Malaysia, digital banking is an emerging trend that is transforming the banking industry. It involves the use of digital technologies to offer customers more convenient, accessible, and personalized banking services. Digital banking in Malaysia is driven by factors such as increasing smartphone and internet penetration, growing demand for more user-friendly banking services, and the emergence of innovative fintech solutions. Digital banks in Malaysia offer a range of digital banking services, such as online account opening, mobile payments, and virtual debit cards, all aimed at providing customers with a more convenient and personalized banking experience. These digital banks typically operate without physical branches, allowing customers to access their banking services entirely through digital channels.
Digital banking in Malaysia is also disrupting the traditional banking industry, prompting traditional banks to invest in digital technologies and offer innovative digital banking services to compete with new players in the market.

II. The State of Digital Banking in Malaysia
The current state of digital banking in Malaysia is rapidly evolving, with the sector experiencing significant growth and competition. Several digital banks have recently launched in Malaysia, including local and international players, each offering a range of digital banking services such as mobile payments, online account opening, and virtual debit cards. The emergence of digital banks in Malaysia has created new opportunities for consumers to access banking services and manage their finances, while also driving innovation and competition in the banking industry. However, the digital banking sector in Malaysia also faces several challenges, including regulatory compliance, customer adoption, and cybersecurity concerns. Despite these challenges, the outlook for digital banking in Malaysia is positive, with continued growth expected in the coming years as more consumers embrace digital technologies for their banking needs. Several factors are driving the growth of digital banking in Malaysia. Firstly, the increasing penetration of smartphones and internet access has made it easier for consumers to access digital banking services from anywhere and at any time. Secondly, the younger and tech-savvy population in Malaysia are more comfortable with using technology for banking, thus leading to greater demand for digital banking services. Thirdly, the COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of digital banking, as more consumers prefer contactless and online banking services. Fourthly, digital banks offer more personalized and user-friendly banking services, which appeal to consumers who are looking for more convenient and affordable banking solutions. Lastly, the emergence of fintech startups and digital banks has disrupted the traditional banking industry, prompting traditional banks to adopt digital technologies and offer innovative digital banking services to compete with new players in the market. All these factors are driving the growth of digital banking in Malaysia and are expected to continue to shape the sector in the coming years.

III. The Benefits of Digital Banking
Digital banking in Malaysia offers several benefits to customers, including convenience, accessibility, and cost savings.
Firstly, digital banking provides customers with greater convenience, allowing them to access banking services at any time and from anywhere using digital channels such as mobile phones, tablets, or laptops. This means that customers no longer have to physically visit a bank branch to access banking services, saving them time and effort. Secondly, digital banking offers greater accessibility to banking services, especially for customers who live in rural areas or have limited access to physical bank branches. With digital banking, these customers can access a range of banking services through their mobile phones or other digital devices, allowing them to manage their finances more easily. Thirdly, digital banking can lead to significant cost savings for customers, as digital banks typically offer lower fees and charges compared to traditional banks. Digital banking also eliminates the need for physical bank branches, which reduces overhead costs for banks and allows them to offer more competitive pricing to customers. In addition to these benefits, digital banking in Malaysia also provides customers with more personalized and user-friendly banking services, such as real-time transaction alerts, automated savings plans, and virtual debit cards. These services are designed to provide customers with a more tailored and convenient banking experience, which ultimately leads to greater customer satisfaction.
In addition to the general benefits of digital banking, there are several specific digital banking services that are popular in Malaysia. One such service is mobile payments, which allow customers to make payments using their mobile phones instead of cash or credit cards. Mobile payments are increasingly popular in Malaysia, with services such as Boost, GrabPay, and Touch 'n Go eWallet gaining widespread adoption. Another popular digital banking service in Malaysia is online remittances, which allow customers to transfer money to other countries using digital platforms such as TransferWise and Western Union. Online remittances are particularly popular among the large number of migrant workers in Malaysia who need to send money back to their home countries. Virtual debit cards are also gaining popularity in Malaysia, allowing customers to make online purchases without the need for a physical card. Digital banks such as BigPay and Aspirasi offer virtual debit cards to their customers, which can be linked to their mobile wallets for easy access and management. Lastly, digital banks in Malaysia are also offering innovative savings and investment products, such as automated savings plans and robo-advisory services. These services provide customers with easy and convenient ways to save and invest their money, with lower fees and minimum investment requirements compared to traditional investment options.

IV. The Impact of Digital Banking on Traditional Banks
Digital banking is disrupting the traditional banking industry in Malaysia by offering customers more convenient, accessible, and cost-effective banking services. Digital banks, without the need for physical branches, can offer lower fees, competitive pricing, and better user experience, putting pressure on traditional banks to adapt and innovate.
Moreover, digital banks are able to leverage big data and advanced analytics to provide more personalized and customized services to customers. They can analyze customer data to understand their financial behavior and offer tailored services such as automated savings plans, investment products, and loans. Digital banking is also creating new opportunities for fintech startups and other digital platforms to enter the banking industry. These new entrants offer innovative solutions and services that challenge traditional banks and create a more competitive environment.
As a result, traditional banks in Malaysia are investing heavily in digital transformation to remain competitive in the changing banking landscape. They are upgrading their digital banking services and partnering with fintech startups to provide customers with more innovative and personalized banking services. Ultimately, this disruption is expected to benefit consumers by providing them with a wider range of choices, lower fees, and more personalized banking services.
To compete with digital banks in Malaysia, traditional banks are implementing various strategies to enhance their digital capabilities and provide customers with a better user experience. One of the key strategies used by traditional banks is to upgrade their existing digital banking platforms to make them more user-friendly and efficient. This includes developing mobile banking apps with advanced features such as biometric authentication, real-time account monitoring, and transaction tracking. Another strategy is to partner with fintech startups to offer innovative solutions and services to customers. These partnerships allow traditional banks to leverage the expertise of fintech startups and integrate their services into their existing banking platforms. Traditional banks are also investing in artificial intelligence (AI) and big data analytics to provide more personalized and customized services to customers. By analyzing customer data, banks can offer tailored services such as automated savings plans, investment products, and loans. Moreover, traditional banks are expanding their online and mobile banking services to reach new customer segments and offer more convenient and accessible banking services. They are also developing digital marketing strategies to promote their services and increase customer engagement.
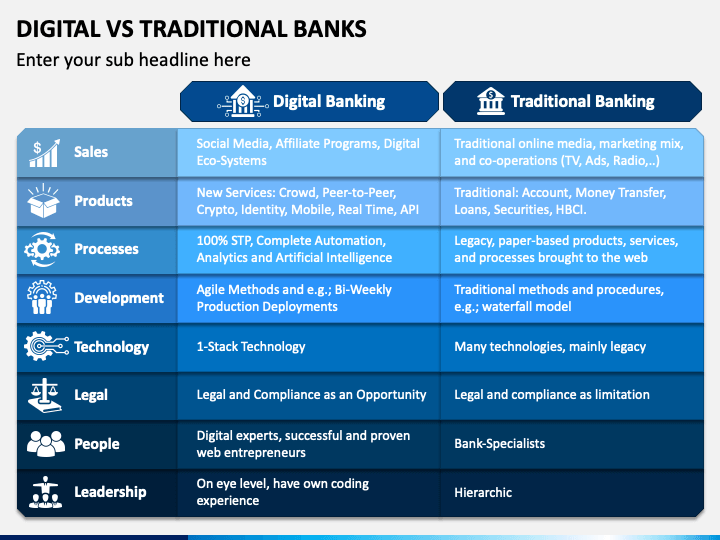
V. The Regulatory Landscape for Digital Banking in Malaysia
The regulatory framework for digital banking in Malaysia is overseen by Bank Negara Malaysia (BNM), the central bank of Malaysia. BNM has issued guidelines and regulations for digital banks to ensure that they operate in a safe and sound manner, protect consumers' interests, and promote financial stability in the country. In December 2020, BNM released a policy document on licensing framework for digital banks in Malaysia. The policy document sets out the eligibility criteria for digital banks, such as minimum capital requirements, ownership structure, and track record of the applicants. It also outlines the regulatory requirements for digital banks in areas such as corporate governance, risk management, and customer protection. To comply with these regulations, digital banks in Malaysia must establish robust risk management frameworks, including anti-money laundering and anti-terrorism financing measures, and implement strong customer authentication and data protection protocols. They must also ensure that their systems and infrastructure meet high standards of security and resilience. However, complying with these regulations can be a challenge for digital banks, especially for new entrants with limited resources and expertise. They may struggle to meet the high capital requirements and establish a track record of financial performance, which are key eligibility criteria for digital banking licenses. Digital banks also face challenges in building trust and credibility with customers who may be wary of new and unfamiliar banking brands. They need to invest in marketing and customer education efforts to build their brand awareness and establish a strong customer base. The competitive landscape in the digital banking sector is rapidly evolving, with new players entering the market and established players expanding their digital offerings. Digital banks need to keep pace with these changes and continuously innovate to stay relevant and competitive.

VI. The Future of Digital Banking in Malaysia
The potential for further growth and development of digital banking in Malaysia is significant, given the country's large population, increasing adoption of digital technology, and supportive regulatory framework. Digital banking is expected to become more pervasive and play a key role in shaping the future of the banking industry in Malaysia. One of the emerging trends in digital banking is the use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to provide personalized and customized banking services to customers. AI-powered chatbots can provide instant customer support and assistance, while ML algorithms can analyze customer data to offer tailored financial products and services.
Another trend is the rise of open banking, which allows customers to share their financial data with third-party providers and access a wider range of financial services. This has the potential to create a more competitive and innovative banking sector, as digital banks can partner with fintech startups to offer new services and solutions to customers.
Mobile payments and digital wallets are also becoming increasingly popular in Malaysia, as customers embrace the convenience and ease of making payments using their smartphones. This trend is likely to continue as more merchants and retailers accept digital payments, and more innovative payment solutions emerge. The use of blockchain technology is also expected to increase in the digital banking sector, offering secure and transparent transaction processing and record-keeping. Blockchain-based solutions can also facilitate cross-border remittances and payments, which is particularly relevant in the context of Malaysia's large population of foreign workers.

VII. Conclusion
Overall, the future of digital banking in Malaysia is bright, with emerging technologies and trends shaping the industry and offering new opportunities for growth and development. As the digital banking sector continues to evolve and mature, it is likely that we will see more innovative solutions and services emerge, transforming the banking experience for customers in Malaysia and beyond.







